結局のところ人間である:アジアの幸福格差の解消
- 公開日:2025/08/25
- 更新日:2026/01/26
- 3065 Views
ウェルビーイング(Well-being)はWell(よい)Being(状態)を組み合わせた言葉で、身体的・精神的・社会的にいい状態であることを示し、持続的な幸福を含む概念を指します。この記事では「Well-being(心身の健康)」として表記します。
今日の成長は、技術だけでは達成されず、根本的なWell-beingのニーズに取り組むことで実現されます。インテージの調査によると、主要ブランドとは、Well-beingを日常生活に組み込むブランドです。それらは繰り返し可能な習慣を創出し、文化や世代に合わせて調整し、共有される成果を提供します。これらのブランドはトレンドを形成し、単に追随するだけではありません。

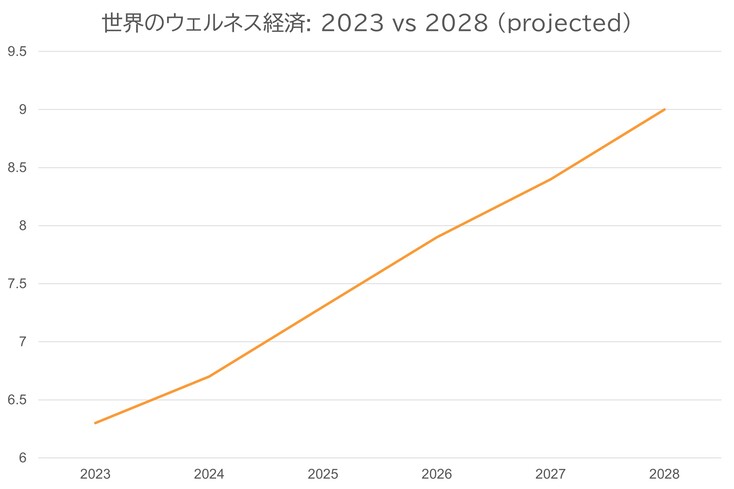
アジアにおけるWell-beingは、急速に拡大する市場であるだけでなく、生産性を高めることが実証されています。需要はすでに供給を上回り、投資収益率はますます定量化可能になっています。世界のウェルネス経済は2028年までに9兆米ドル(約1,380兆円)に達すると予測されています(GWI、2024年)。
職場における精神疾患は、年間推定120億労働日分の損失と関連し、生産性において約1兆米ドル(約150腸炎)のコストを生んでいます(WHO, 2024)。 雇用主による行動健康支援制度は、100米ドル(約15,000円)投資ごとに190米ドル(約29,000円)の医療費削減効果を示しています(JAMA Network Open, 2025)。一方、メンタルヘルスの社会的決定要因を改善することは、地域モデルにおいて大きな正味利益をもたらします(Nature Mental Health, 2025)。
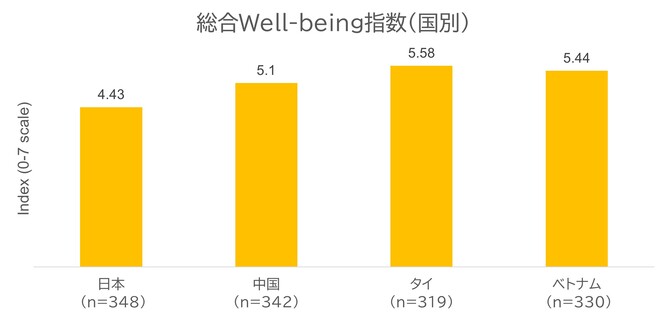
インテージが日本・中国・タイ・ベトナムで実施した最新のWell-being調査では、幸福度にばらつきが確認されました。総合Well-being指数を最も大きく左右する要素は、同時に最も支援が行き届いていない領域でもあります。社会的・経済的・精神的Well-beingは総合指数に最も大きな影響を与える一方で、満足度の面で顕著な格差が存在します。
インテージの4段階複合指標は行動と認識を統合した指数です:
(1) 6次元(身体的・精神的・社会的・経済的・環境的・目的/精神的)における次元スコアリング
(2) 多重共線性を除去するための因子分析
(3) 要因の重み付けのための回帰分析
(4) 単一Well-being指数への統合
これにより6次元にわたるの同次元比較が可能となります。
・全体像
Well-being指数は国によって異なり、緊張感が最も高いのは日本です。タイとベトナムは比較的良好な結果を示していますが、若年層には依然として弱点が認められます。
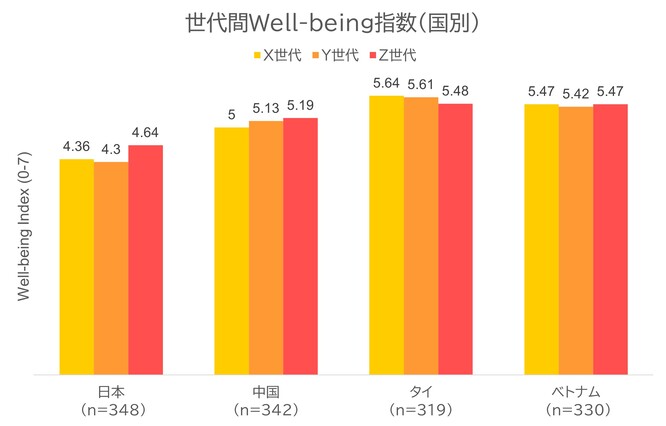
・世代間ギャップに注意:世代ごとの空白
一般的に、Z世代は向上心があるが地に足をつける必要があり、Y世代は繋がりとバランスを求め、X世代は日常と安定を重視します。
・日本 — 「秩序は保たれているが、緊張状態にある」
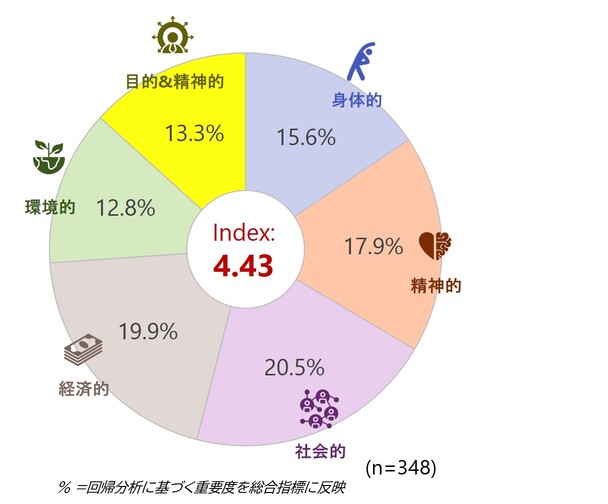
日本のWell-beingの状況は、強い秩序感と責任感を反映しつつも、より深い感情的な充足感への明確な必要性を示しています。日本の世代別ではZ世代が最も高いスコアを示していますが、他国の同世代と比較すると依然として控えめな水準です。
社会的・経済的・精神的Well-beingが上位3つの要因だが、精神的Well-beingは一貫して低い水準にあり、感情的つながりを深める余地があることを浮き彫りにしました。
・中国 — 「確信に根ざし、完全性へと向かう」
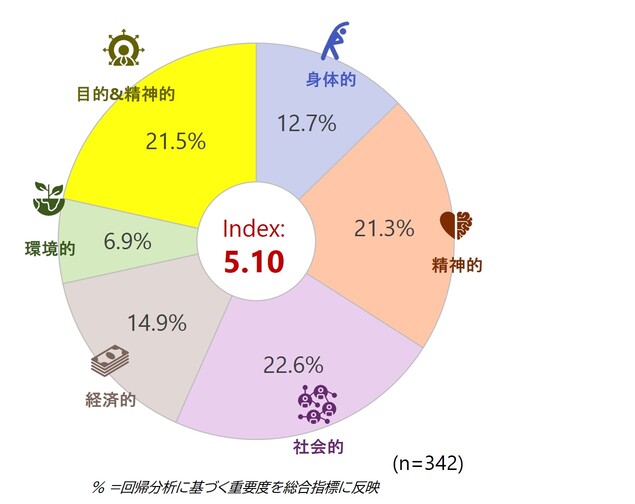
中国の消費者は、「目的と精神性」の次元において最も高い志向性を示しており、特にZ世代で顕著です。これはアイデンティティと意味を通じてつながる強力な機会を示唆しています。
・タイ — 「高エネルギー、隠れた圧倒感」
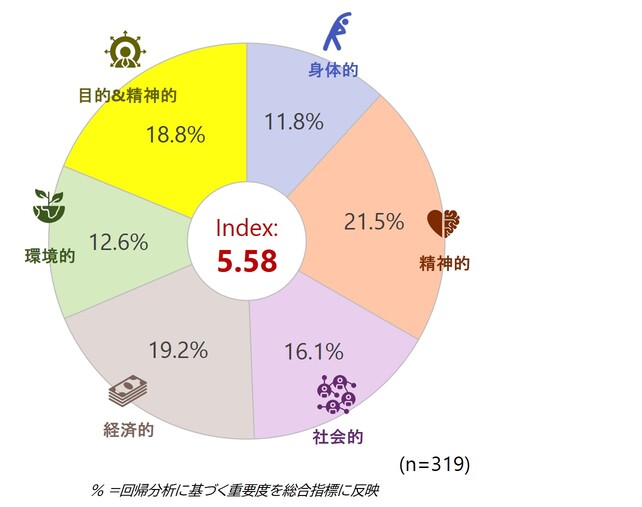
タイは総合指数で首位を占める一方で、Z世代は最低スコアを記録——潜在的な感情的ストレスを示唆しています。
世代ごとに要因はは異なる:X世代は経済的、Y世代は社会的、Z世代は精神的側面で、経済的圧力は軽減されているにもかかわらず、タイのZ世代は感情的な要求に押し潰されているように見えます。
・ベトナム — 「バランスの取れた基本、レベルアップの準備は整った。」
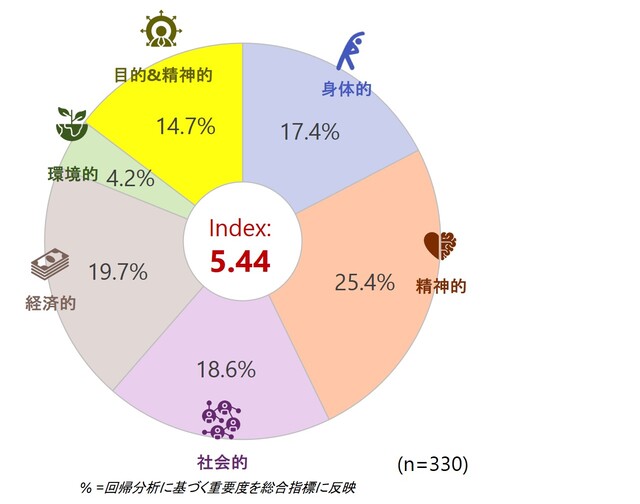
ベトナムでは世代を問わずバランスの取れた幸福感が示され、安定性を示す一方で、内なる目的意識のギャップも浮き彫りになっています。
Z世代においては、社会的つながりが内面的な要素よりも幸福度を強く牽引しています。これはブランドが意味や方向性を提示する機会を生み出しています。
11カ国の定量データを即座に活用Global Viewer
世界11カ国・数万人規模のアンケート結果を凝縮した「定量ストックデータ」サービスで、主要カテゴリーの購買行動や意識を国間比較分析。ゼロから調査を企画する時間を省き、スピーディーに対象者理解。
次元別インサイト
経済的Well-being:現在と将来のギャップが最大
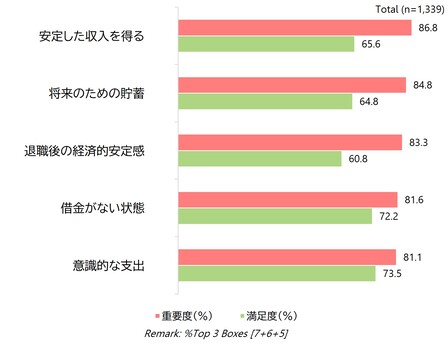
人々は安定性と老後の保障を重視する一方で、長期的な計画はまだ習慣化されていません。中国は金融規律において先行しており、自己啓発と投資から自信を得ています。
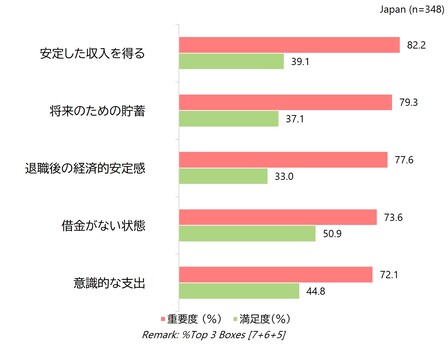
対照的に、日本は最も深刻な経済的圧力に直面しており、所得安定への敏感さが重要度と満足度の大きな乖離を招いています。
精神的Well-being:見過ごされがちだが強力な推進力
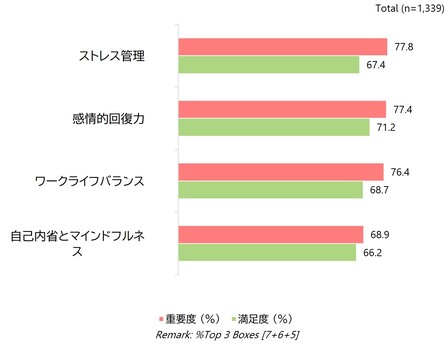
メンタルヘルスは財務上の優先事項よりも低い順位に置かれることが多いものの、あらゆる市場に潜在的な影響を及ぼしています。ストレス管理には最大のギャップが見られ、効果が実証済みの活動(例:マインドフルネス、ヨガ)は依然として十分に活用されていません。
ブランドは精神的ウェルビーイングを「隠れたレバレッジ」と捉え、ストレス軽減、レジリエンス、睡眠、社会的支援の機能を製品・サービスに組み込むことができます。
社会的Well-being:家族との絆が最も重要
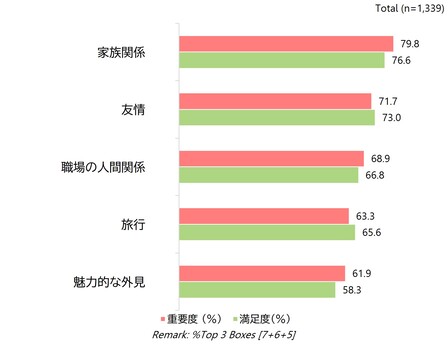
家族は社会関係の中で常に最高位を占め、その差は概して小さいです。
外見も影響貢献しており、特に日本ではメイクが若年層の自信を高めています。タイと中国では旅行が主要な推進要因である一方、ベトナムではソーシャルメディアがより強い役割を果たしています。
重要なポイント
アジア全域で、消費者は「豊かに生きる」意味を再定義しています——社会的つながりから経済的安定、そしてその先へと広がりつつあります。各領域がブランドに人間の価値観と結びつき、意図を習慣へと変える機会を提供します。先進的なブランドはWell-beingを単にマーケティングするだけでなく、戦略的・文化的・一貫性を持って実践しています。
1) 次元を横断して統合
Well-beingの複数側面(例:精神的×身体的×環境的)を結びつけるプラットフォームを設計します。
アリペイ「アントフォレスト」(中国):環境・身体・社会・目的意識に跨る多次元設計図。地域生計への波及効果も。ユーザーは低 炭素行動で「グリーンエネルギー」を獲得。仮想の木は乾燥地域で実在の木に(2025年アースデイまでに約6億本)。アプリは歩行/自転車/公共交通を報酬対象とし、アリペイや提携先で行動を追跡。日常的な移動を促進。 ソーシャル機能——友人とのエネルギー共有、リーダーボード、共同水やり、可視化された「実在の樹木」マイルストーン——が継続的な関与を促進。NGO/政府と連携した砂漠化地域での植樹は農村雇用と管理意識を創出し、プログラムを地域文化・経済に根付かせる。
2) キャンペーンではなくコミュニティを創る
貢献、学習、感情的なつながりを可能にする常時稼働型コミュニティを構築します(逆ではない)。
VinFast(ベトナム):インフラを複数のウェルビーイング要素(環境・社会・精神・身体・経済)に対応するコミュニティシステムとして位置付ける。VinFastはオーナー主導の活発なフォーラム(充電・メンテナンス・ノウハウ・トラブルシューティング)を運営し、ユーザーをメンター化することでEV不安を軽減。オーナー主導のコンテンツとブランド提携が継続的な情報共有と新規参加者を創出。コミュニティへの貢献を「単なるファン活動」ではなく「市民的貢献」と再定義する。
3) 世代別の購買意欲を喚起する
購買力は移行中です。Z世代の消費額は2030年までに約12兆ドル(約1,800兆円)に達し、アジア太平洋地域のZ世代は既に予防医療・小売・デジタルヘルス分野で主導権を握っています(Bain, 2023)。Z世代の購買力変化に対応し、長期目標を現在進行形の小さな成功体験に変換させましょう。
ポケモンSleep(日本):健康行動を低摩擦のゲームループに変換。枕元にスマホを置く(または腕時計/GO Plus+と連動)だけで睡眠が分類(うたた寝/居眠り/熟睡/バランス)され、日替わり報酬が獲得可能。 メカニズムは世代特性に連動:Z世代は月次ソーシャルイベントで結束(「みんなで一緒にやる」)、Y世代は居心地の良いセルフケアと収集要素を享受、X世代はシームレスなデバイス連携による自動化と制御を重視。
ブランドが単なるウェルビーイングの提唱を止め
明確な施策と文化的配慮を持って実践し始めるとき
トレンドを追う立場から
トレンドを創る立場へと移行する
アジアは単一の市場ではありません。それは儀式、人間関係、現実が織りなすモザイクです。インテージはそのモザイクを、地域に最適化され世代 を意識した、貴社ブランドのための実用的な習慣へと変換します。私たちの役割は、貴社が展開する商品が日常生活に確固たる地位を築き、時間の経過とともに選好と価格決定力を獲得することを保証するすることです。
今日を知り、明日を動かす。インテージはアジアを最も深く理解している。

参考文献
Global Wellness Institute (2024). 2024 Global Wellness Economy Monitor.
Bain & Company (2023). アジア太平洋地域の消費者——より良い成果/体験のために追加費用を支払う意思。
NIQ & World Data Lab (2024). 「Spend Z」レポート:2030年までにZ世代のグローバル消費額は約12兆ドルに。
WHO (2024). 職場におけるメンタルヘルス:ファクトシート(120億労働日損失;約1兆米ドルのコスト)。
JAMA Network Open(2025年)。強化された行動医療サービスの投資収益率:100ドル投資あたり190ドルの節約。
McKinsey Health Institute (2025). 未来への投資―メンタルヘルスの改善がもたらす普遍的利益。
※当該記事は、原文(英語)を機械翻訳のうえ記載しています。
-

執筆者プロフィール
ダンジャイタウィン・アナタチャイ(オーム)
オームは、タイで高い評価を受けるマーケティング分析と持続可能なマーケティングのコンサルタントの一人であり、25年以上の経験を有しています。彼女の専門知識は、消費者心理、データ駆動型戦略、人間中心のイノベーションを結びつけ、組織が変化する消費者価値観と一致させることを支援します。
文化の動向の変化と目的志向のマーケティングに対する深い洞察を活かし、オームは企業がいまや将来の世代にわたって真に重要なものに根ざしたレジリエンス、関連性、関係性の深みを育むため、短期的な成功を超えて持続可能な成長を促進します。
 Global Market Surfer
Global Market Surfer CLP
CLP
